Step1
Carbon Reduction Scope
Total Carbon Emissions of a Company
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol breaks down a company’s carbon emissions to be inventoried into scope1, scope 2, and scope 3.
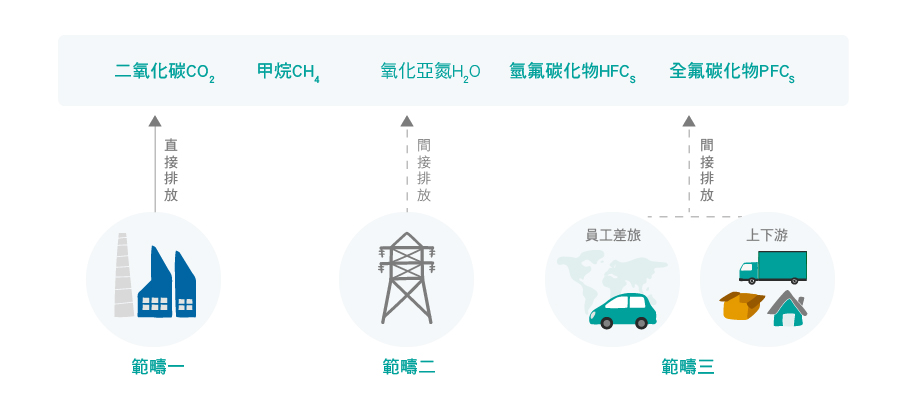
- Scope 1: GHGs emitted directly from the manufacturing process of a company, e.g., cement manufacture and fuel combustion.
- Scope 2: GHGs emitted during the consumption of purchased energy (e.g., electricity, heat, or steam) during the manufacturing process of a company, e.g., a company’s carbon emissions released from its use of electricity provided by TPC’s coal-fired power plants.
- Scope 3: Indirect emissions that result from business activities and have noting to do with self-owned or controlled assets. Sources of this emission scope include emissions from leasing, commute, purchase from upstream vendors, or delivery of goods to downstream shipping companies.
Carbon Footprint of Products
- This includes all carbon emissions released throughout the life cycle of products, from raw materials mining, assembly, transportation, product use, to disposal/recycling.

-
What is Carbon Footprint Label?
Product carbon footprint information undergone rigorous review process then is conveyed to consumers.

-
In 2019, E.SUN became the only bank in Taiwan to issue only carbon neutral credit cards.�
Each newly issued E.SUN credit card passes dual certification of “carbon label” and “carbon neutral”.
Step3
Obtain certification
What is obtainment of certification?
That is the process of a third party reviewing a company’s carbon inventory report and issuing a review report or statement.
Commonly seen certifications include ISO 14064, ISO 14067, and PAS2060.
- ISO 14064: It mainly audits a company’s carbon consumption, and comprises two types:
- ISO 14064-1 (Basic inventory): It mainly assists enterprises to define GHG emission boundaries; quantify GHG emissions; and establish GHG management procedures.
- ISO 14064-2 (Carbon reduction actions): It mainly assists enterprises in developing projects stipulating GHG emission reduction goals.
- ISO14067: It mainly audits product carbon footprint by using science-based approaches to calculate total direct/indirect emissions throughout the "product life cycle", from raw materials purchase, design, manufacturing, packaging, shipping, marketing, use by consumers, to disposal.
- PAS2060: It helps enterprises neutralize their carbon emissions or product carbon footprint through voluntary reduction and offsets.
Step4
Setting Carbon Reduction Goals
Setting self-goals
Ordinary enterprises may set carbon reduction goals at their will, e.g., annual reduction in carbon emissions by 5%; doing so can be advantageous as they can tailor the goal according to their state of operations, but it might not be aligned with internationally accepted ones. Therefore, most large enterprises refer to the standards promulgated by international initiative organizations. Below is an example taken on SBTi, an international initiative partnership.
Participation in SBTi, an International Initiative Partnership
What is SBTi?
- SBTi stands for Science Based Target initiative, which is a partnership between the United Nations Global Compact, World Resources Institute, and World Wildlife Fund.
- Science-based approaches are adopted for the calculation of a reasonable carbon emission credit for specific industries and companies; this allows them to establish targets for carbon reduction on the basis that the global temperature rise will not exceed 1.5°C.
Participation Process?

Commitment


Set SBTs


Submit targets and complete review


Disclose carbon reduction targets externally


Disclose execution progress every year
E.SUN setting SBTs
E.SUN FHC was the first financial institution in Taiwan and second in Asia to pass SBT review. The scope of emissions included the business operations of E.SUN and its investment and financing positions, which are most critical. E.SUN systematically and strategically moves towards its goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C and achieving net zero emissions by 2050, which is aligned with the 2050 Net-zero Emissions objective.
You may also join E.SUN ESG and sustainability initiative
E.SUN ESG and sustainability initiative participants setting concrete goals to mitigate climate change will be provided with consultation, initiative column, and invitation to participate in CSR activities.
Step5
Carbon Reduction Strategy
Scope 1: Carbon Emissions Reduction from Operations
- Use energy-efficient equipment, low-carbon equipment, and carbon capturing equipment.
- How will E.SUN help? We provide sustainable finance such as financing energy-efficient equipment, green financing, and sustainability-linked loans.
More
Scope 2: Electricity Conservation and Use of Renewable Electricity
- Use energy-efficient equipment or constructing green buildings
- Adopt/Purchase renewable electricity
- Buy renewable electricity certificates
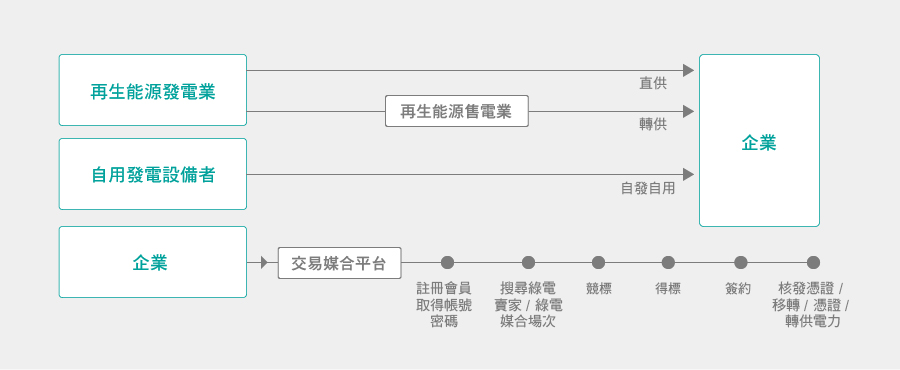
- How will E.SUN help? We provide renewable energy project, green building financing, and Solar Panel Rooftop Loan.
Scope 3: Supply Chain Management
- How will E.SUN help? We provide supply chain finance and external consultants-offered consultation.
Contact Us

















